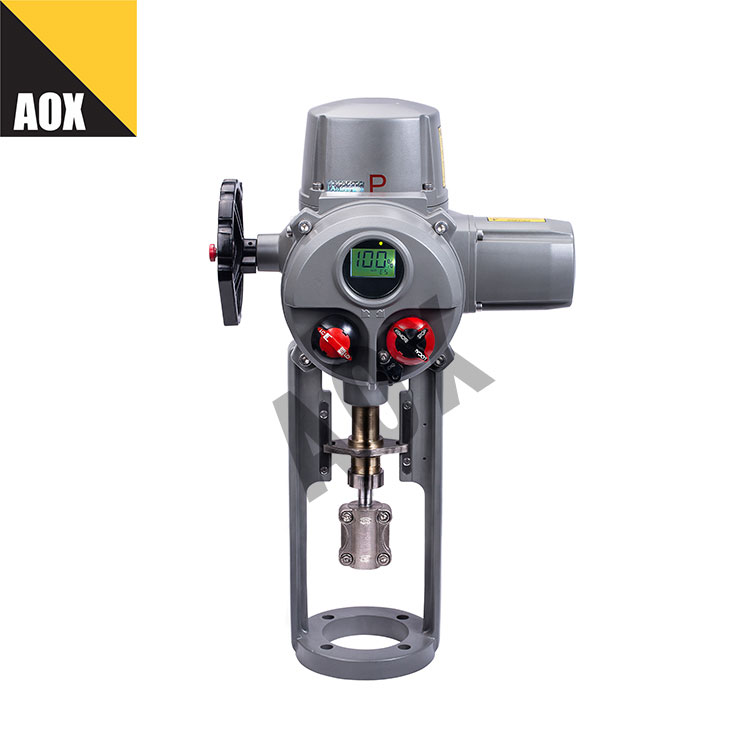
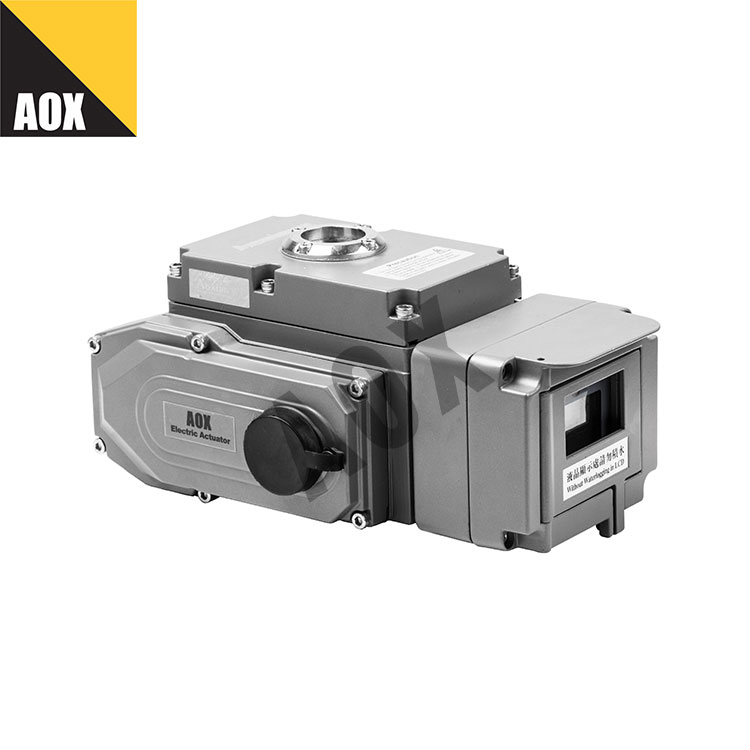
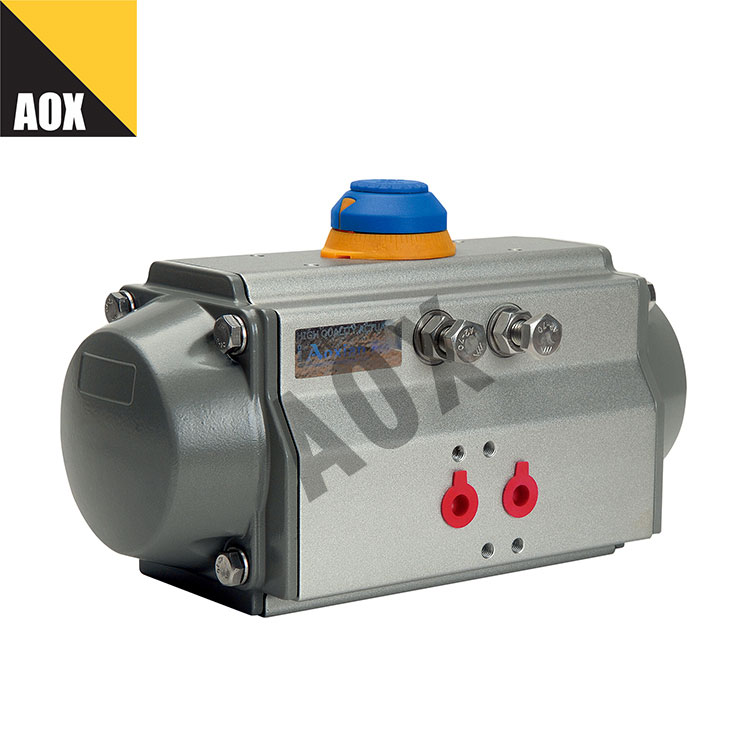
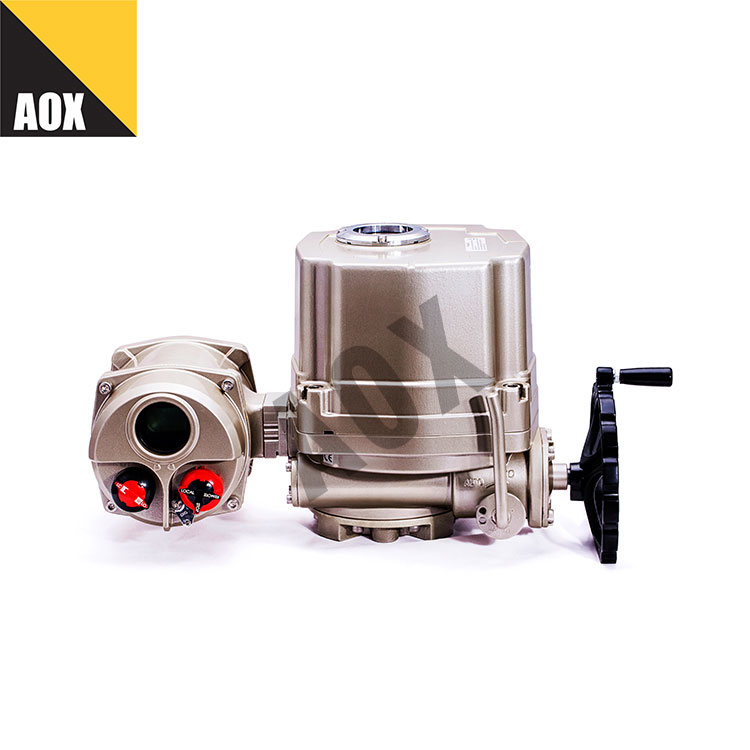
Single Acting Pneumatic Actuator is a type of actuator that uses compressed air to drive a piston and convert energy into motion. The actuator can be used to control various industrial valves, such as ball valves, butterfly valves, and gate valves. The structure of the single acting pneumatic actuator includes a cylinder, piston, end caps, and spring. When the compressed air enters the cylinder, it pushes the piston to move in one direction, and the energy stored in the spring is used to push the piston back when the air pressure is released.

What are the advantages of a Single Acting Pneumatic Actuator?
The advantages of using a single acting pneumatic actuator include its simplicity, fast response time, and high durability. The actuator has few moving parts, making it easy to maintain and repair. It also responds quickly to changes in air pressure, making it ideal for applications that require rapid adjustments. Additionally, the actuator is designed to withstand harsh environments and heavy loads, providing long-lasting performance for industrial applications.
What are the applications of Single Acting Pneumatic Actuators?
Single acting pneumatic actuators are widely used in various industries, such as chemical processing, oil and gas, and water treatment. The actuators can be used to control valves that regulate the flow of liquids or gases in pipelines. They are also used in the automation of manufacturing processes, such as in the production of automobiles, food products, and electronics. In the construction industry, the actuator is used to control the movement of heavy machinery and equipment.
How to maintain a Single Acting Pneumatic Actuator?
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure that the actuator functions properly and lasts a long time. The actuator should be inspected periodically for signs of wear and tear, such as leaks or rust. The protective coating on the cylinder and end caps should be inspected and replaced if damaged. The actuator should also be cleaned regularly to prevent the buildup of dust and debris. Lubrication is also essential to prevent friction and ensure smooth operation.
What is the difference between a Single Acting Pneumatic Actuator and a Double Acting Pneumatic Actuator?
The main difference between a single acting pneumatic actuator and a double acting pneumatic actuator is that the former uses only one side of the piston to generate force, while the latter uses both sides. As a result, double acting pneumatic actuators are more versatile and can be used in a wider range of applications. They are also more expensive and complex than single acting pneumatic actuators.
In conclusion, single acting pneumatic actuators are widely used in various industrial applications due to their simplicity, durability, and fast response time. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure that the actuator functions properly and lasts a long time.
Zhejiang Aoxiang Auto-Control Technology CO.,Ltd (Aox Actuator) is a professional actuator manufacturer, specializing in the production of electric actuator, pneumatic actuator, and hydraulic actuator. Our products are widely used in industrial pipelines, water treatment, and environmental protection. For more information about our products and services, please visit our website https://www.aoxactuator.com or contact us at zjaox@zjaox.com.
References:
1. Furuta, K., & Yamamoto, K. (2014). Design of single-acting pneumatic cylinder control system for creating time-varying haptic sensations. IEEE Transactions on Haptics, 7(3), 367-376.
2. Wu, B., He, L., Xu, X., & Yu, J. (2016). Nonlinear modeling and position control of a single-acting pneumatic cylinder. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 24(3), 1007-1014.
3. Deng, Q., Shi, H., & Yu, W. (2017). Design and experiment of a parallel mechanism with single-acting pneumatic muscle actuators. Robotica, 35(11), 2177-2189.
4. Zhao, H., Wang, H., He, L., & Xu, X. (2015). Energy-based control of a single-acting pneumatic artificial muscle driven exoskeleton for knee joint rehabilitation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 23(3), 380-390.
5. Liu, X., He, L., & Xu, X. (2018). Output-feedback sliding mode control for a single-acting pneumatic artificial muscle and its application in knee rehabilitation exoskeleton. Control Engineering Practice, 72, 1-15.
6. Li, Y., Li, L., Wu, X., & Cao, D. (2019). Active disturbance rejection control of a single-acting pneumatic muscle system. ISA Transactions, 89, 245-253.
7. Chen, L., & Gao, Z. (2015). Ankle rehabilitation training based on a pneumatic single-acting actuator. Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology, 15(05), 1550055.
8. Zhang, X., Zhao, H., & He, L. (2017). Neuromuscular-inspired control for a single-acting pneumatic artificial muscle based knee rehabilitation exoskeleton. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine, 231(4), 385-396.
9. Zhang, C., Wang, J., Guo, Y., & Zhang, J. (2018). Design and experimental study on the grasping force control system of single-acting pneumatic muscle prosthetic hand. Measurement, 129, 445-451.
10. Zhao, H., & He, L. (2018). Modelling and identification of a parallel mechanism based on single-acting pneumatic muscle actuators for human ankle rehabilitation. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 15(2), 1729881418759776.
 English
English  Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик 





